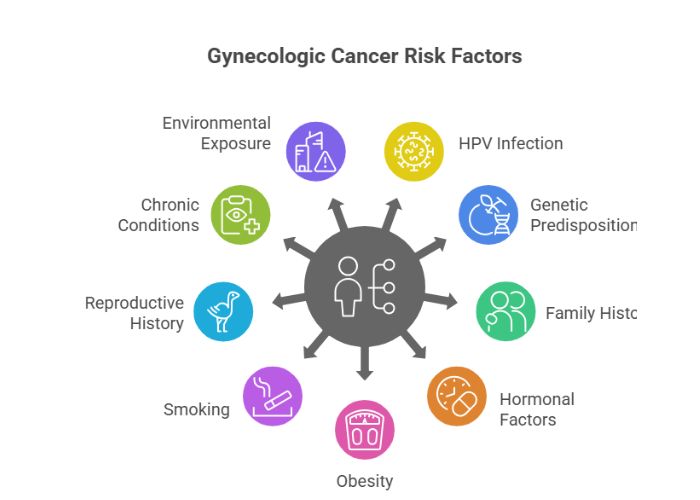
Understanding the causes and risk factors helps women take preventive steps. Key contributors include:
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): High-risk strains (HPV-16, HPV-18) linked to cervical and vulvar cancers.
- Genetic Predisposition: BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations or Lynch syndrome increase ovarian and uterine cancer risk.
- Family History: Relatives with breast or gynecologic cancers raise vulnerability.
- Hormonal Factors: Prolonged estrogen exposure (early menstruation, late menopause, hormone therapy) heightens risk.
- Lifestyle & Health: Obesity, smoking, chronic conditions like endometriosis or PCOS can increase risk.
- Reproductive History: Never having children or late pregnancies may raise ovarian cancer risk.
- Environmental Exposure: Talc, asbestos, or certain chemicals may play a minor role.